To read in-depth about Resonance architecture, reference the architecture
page.
Heterogeneous blockchains
Blockchain transactions have become increasingly heterogeneous:Heterogeneous in this context means increasingly complex and different or
unique in nature.
- Bitcoin supported only simple arithmetic operations (e.g. transfers)
- Ethereum introduced smart contracts, enabling transactions to execute arbitrary logic
- Blobs (EIP-4844) introduced transactions to store blobs of data on Ethereum
- Solana, Monad, and MegaETH introduce parallel transaction execution
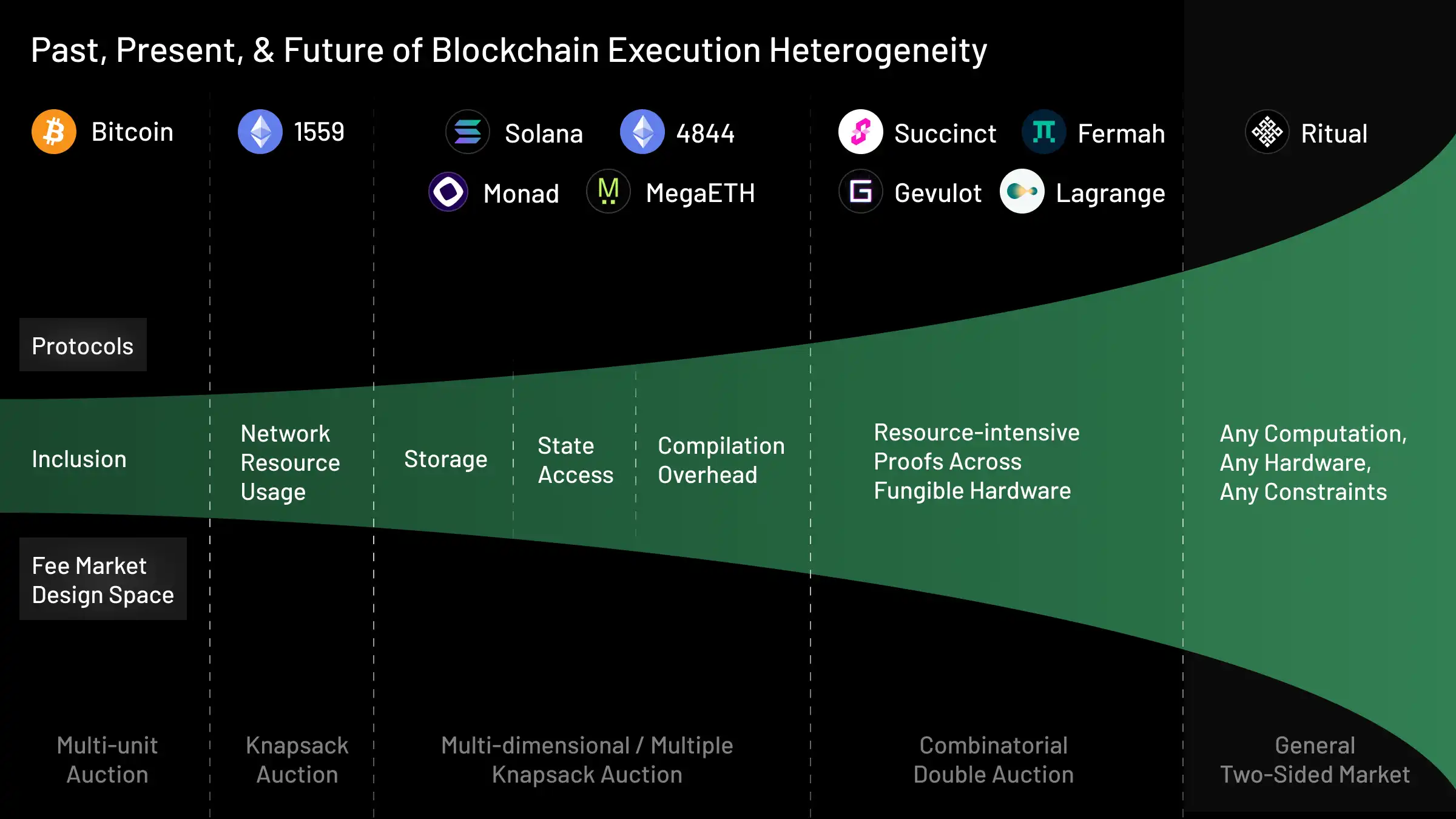
Transaction heterogeneity grows exponentially.
Existing fee mechanisms are insufficient
As we scale the paradigm of what is possible with blockchain transactions, we start to see that existing fee mechanisms are insufficient in supporting this heterogeneity.A fee mechanism is a mechanism by which blockchains price execution of
transactions. The simplest mechanism is a first-price auction, akin to a
bidding war, where transactions that pay the highest fees, irrespective of
what they are executing, are included.
- Suffers from poor welfare guarantees as the number of dimensions (aka degree of heterogeneity) increases
- Requires the hardcoding of the set of resources into the protocol, which can only be updated via hard forks
- Faces information-theoretic challenges in setting the right base fees across many dimensions
Increased Costs
Complex transactions become expensive as the mechanism fails to price them efficiently
Limited Support
New transaction types that are not hard-coded into the protocol are unsupported
Pricing Complexity
Users struggle to set appropriate fees when transactions involve complex
execution logic
Failed Execution
Transactions fail when the fee mechanism cannot efficiently scale to meet demand
Resonance is the answer
Resonance is a new, state-of-the-art fee mechanism built for heterogeneous compute with a two-sided market setting (matching users to nodes).Resonance for users
- Each transaction specifies a
valuationit wants to pay for execution - Transactions can be executed by single nodes or multiple nodes
- Users can choose to prioritize speed or cost when submitting transactions
- Users can execute any type of compute, without protocol-level constraints
- Transactions can execute privately via multi-party assignment
Resonance for nodes
- Nodes specify a
cost functionfor each transaction, granularly dictating execution costs - Nodes can specialize in specific types of compute, e.g. AI inference
- Nodes can execute any type of compute, without protocol-level constraints
- Nodes can execute unconflicting transactions in parallel
Resonance for the network
- Transactions are efficiently matched, optimizing for both cost and speed
- Node capacity is optimally allocated
- Users have full preference over transaction execution
- With Symphony, parts of the network can be specialized
Brokers
Under the hood, Resonance works by introducing a new entity known as a broker. Brokers are sophisticated, profit-seeking agents that compute matchings between transactions and nodes.Consider the parallel to brokers as block builders or MEV searchers: advanced
participants that use their informed priors to efficiently match transactions,
pocketing the spread between transaction
valuation and node execution cost
in the process.Future work
We plan to extend Resonance in several key areas to hyperscale modern apps and protocol usage:- Scheduled transactions can be natively priced to enable use cases like agents on-chain to be economically efficient
- No need to trust Ritual anymore for running the auctioneer: anyone can run it
- Increased TPS for heterogeneous transactions priced via Resonance as we allow for streaming settings
- Research into posted price mechanisms to enable users to have an experience similar to Uber for pricing transactions
Further reading
For more information on Ritual’s fee mechanism, see our blog posts and academic paper:
Resonance: A Market Mechanism for Heterogeneous Computation
Resonance enables heterogeneous computation on-chain. This post builds
towards a formal definition of the heterogeneous setting.

The Resonance Mechanism and its Properties
This post gives a formal description of the Resonance mechanism and the
desiderata it satisfies.

arXiv: Resonance: Transaction Fees for Heterogeneous Computation
This paper introduces Resonance: a new kind of transaction fee mechanism for
the general two-sided market setting (with users on one side and nodes on
the other), where both sides of the market exhibit a high degree of
heterogeneity.

